key concepts
- Warps: In CUDA, a warp is a fundamental execution unit in the GPU. It represents a group of threads that are executed together in a SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) fashion on a single GPU core. In CUDA, each group of 32 consecutive threads is called a warp. A Warp is the primary unit of execution in an SM. Once a thread block is allocated to an SM, it will be further divided into a set of warps for execution.
- Stream Multiprocessor (SM)
The CUDA architecture is built around a scalable array of multithreaded Streaming Multiprocessors (SMs). When a CUDA program on the host CPU invokes a kernel grid, the blocks of the grid are enumerated and distributed to multiprocessors with available execution capacity. The threads of a thread block execute concurrently on one multiprocessor, and multiple thread blocks can execute concurrently on one multiprocessor. As thread blocks terminate, new blocks are launched on the vacated multiprocessors
Each SM contains 8 CUDA cores, and at any one time they’re executing a single warp of 32 threads - so it takes 4 clock cycles to issue a single instruction for the whole warp. You can assume that threads in any given warp execute in lock-step, but to synchronise across warps, you need to use__syncthreads()
memory
- shared_memory: https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/using-shared-memory-cuda-cc/
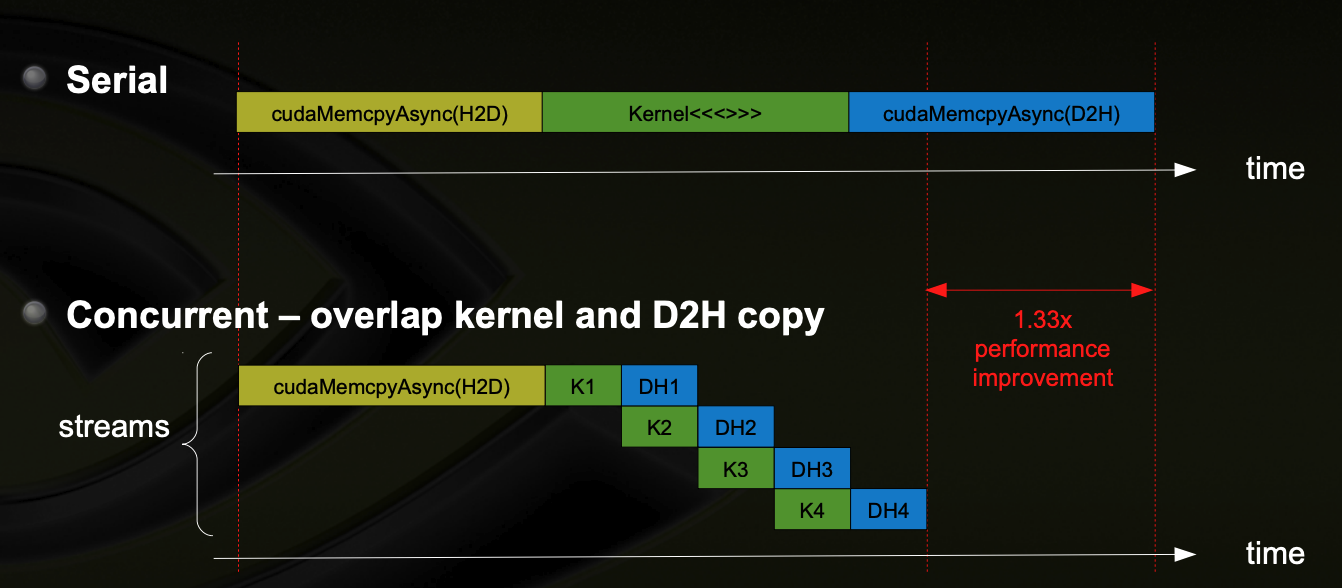
- Page-Locked Host Memory
stream
A sequence of operations that execute in issue-order on the GPU
- CUDA operations in different streams may run concurrently
- CUDA operations from different streams may be interleaved
event
events are synchronization mechanisms used to measure and manage time, particularly for timing purposes and performance profiling.
- event creation
1
2
3
4
5
cudaEvent_t startEvent, stopEvent;
cudaEventCreate(&startEvent);
cudaEventCreate(&stopEvent); - record eventHere,
1
2
3cudaEventRecord(startEvent, 0);
// ... GPU code to be timed ...
cudaEventRecord(stopEvent, 0);cudaEventRecordrecords the current time in the events startEvent and stopEvent. The second argument,0, specifies the stream in which to record the event (0 means the default stream). - synchonize eventsThis function call makes the CPU wait until the GPU has completed all tasks associated with the stopEvent.
1
cudaEventSynchronize(stopEvent);
- Calculate Elapsed Time
1
2float milliseconds = 0;
cudaEventElapsedTime(&milliseconds, startEvent, stopEvent); - destroy event
1
2cudaEventDestroy(startEvent);
cudaEventDestroy(stopEvent);
keywords
global functions that are executed on the GPU, called from CPU
device functions that are executed on the GPU, called within GPU
shared
align is a compiler directive that can be used to specify alignment requirements for variables in device code.
__launch_bounds__
the launch_bounds attribute is used to specify launch bounds for a kernel function. The launch bounds control the number of threads per block and the maximum number of blocks per multiprocessor for a specific kernel.1
__launch_bounds__(maxThreadsPerBlock, minBlocksPerMultiprocessor)
macros
- CUDACC is a predefined macro in CUDA C/C++ that is used to determine whether the code is being compiled by the NVIDIA CUDA C/C++ compiler (nvcc).
- NVCC is a predefined macro that is automatically defined by the NVIDIA CUDA compiler (nvcc). It allows you to conditionally compile code based on whether the code is being processed by the CUDA compiler or a regular C++ compiler
usage
the triple-chevron notation <<<...>>> is used to specify the execution configuration of a CUDA kernel launch.
1 | kernel<<<gridDim, blockDim, sharedMem, stream>>>(...); |
gridDim: Specifies the dimensions of the grid (number of blocks). It can be a 1D, 2D, or 3D configuration, specified as (gridDimX, gridDimY, gridDimZ).blockDim: Specifies the dimensions of each block (number of threads per block). It can also be a 1D, 2D, or 3D configuration, specified as (blockDimX, blockDimY, blockDimZ).sharedMem: Optional parameter specifying the dynamic shared memory per block in bytes. If not specified, it defaults to 0.stream: Optional parameter specifying the CUDA stream in which the kernel should be executed. If not specified, it defaults to the default stream (0).