trie
a trie, also called prefix tree, is a type of k-ary search tree. These keys are most often strings, with links between nodes defined not by the entire key, but by individual characters. In order to access a key, the trie is traversed depth-first, following the links between nodes, which represent each character in the key.
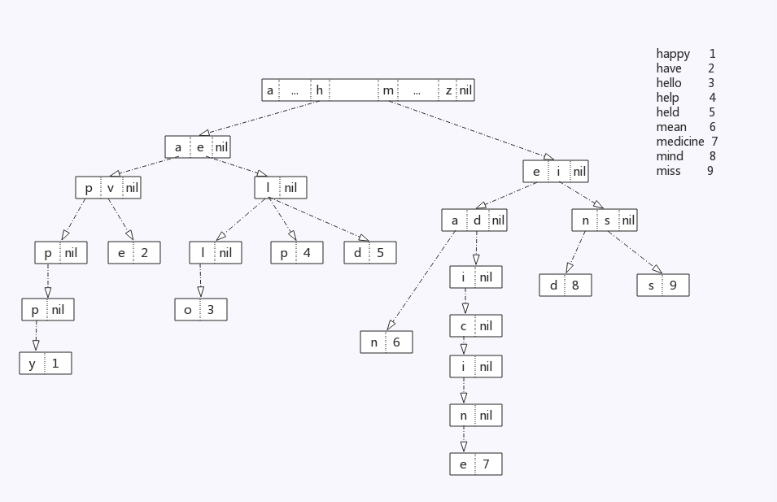
In general, the nodes of a Trie look like this:
1 | [ [Ia, Ib, … I*], value] |
[Ia, Ib, … I*] is the index array of the node, which takes the next character in the key as the index, and each element I* points to the corresponding child node. value represents the value
MPT
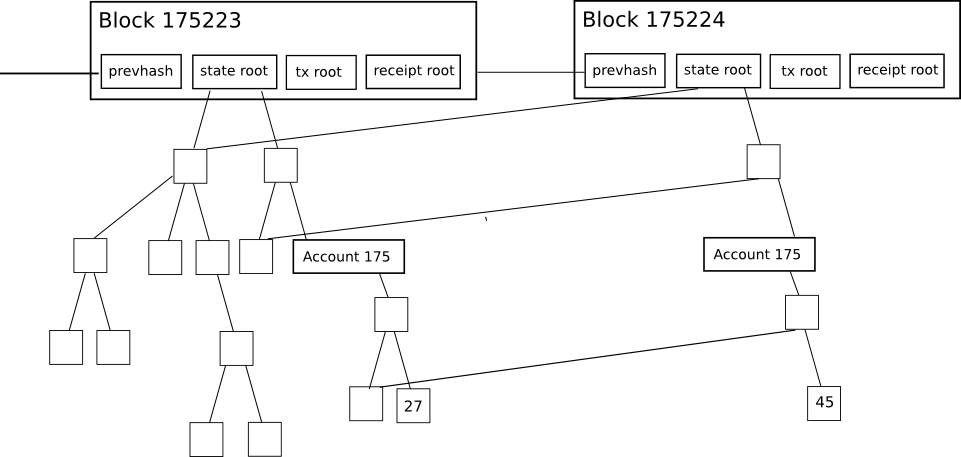
Each block of Ethereum contains three MPT trees, respectively
- Transaction tree
- Receipt tree
- State tree
In the figure below are two block headers, where state root, tx root receipt root stores the roots of the three trees, and the second block shows when the data of account 175 changes (27 -> 45). Only need to store 3 nodes related to this account, and the data in the old block can still be accessed normally. (This is somewhat similar to the implementation of an immutable data structure in a functional programming language.) The detailed structure is
- use []byte as key, other than string
- nibble: the smallest unit of the key type (4 bit)
- Use hashes to refer to nodes instead of memory pointers
there are two types of node: full nodes (fullNode) and short nodes (shortNode). Full nodes have 17 elements, while shortNode nodes have two elements. Their schematic expressions are as follows
1 | fullNode: [i0, i1, i2, … i15, hash] |
if the hash pointing to a value, it is a leaf node; if pointing another node, a non leaf node. shortNode contains extension and leaf node. full node is branch node.
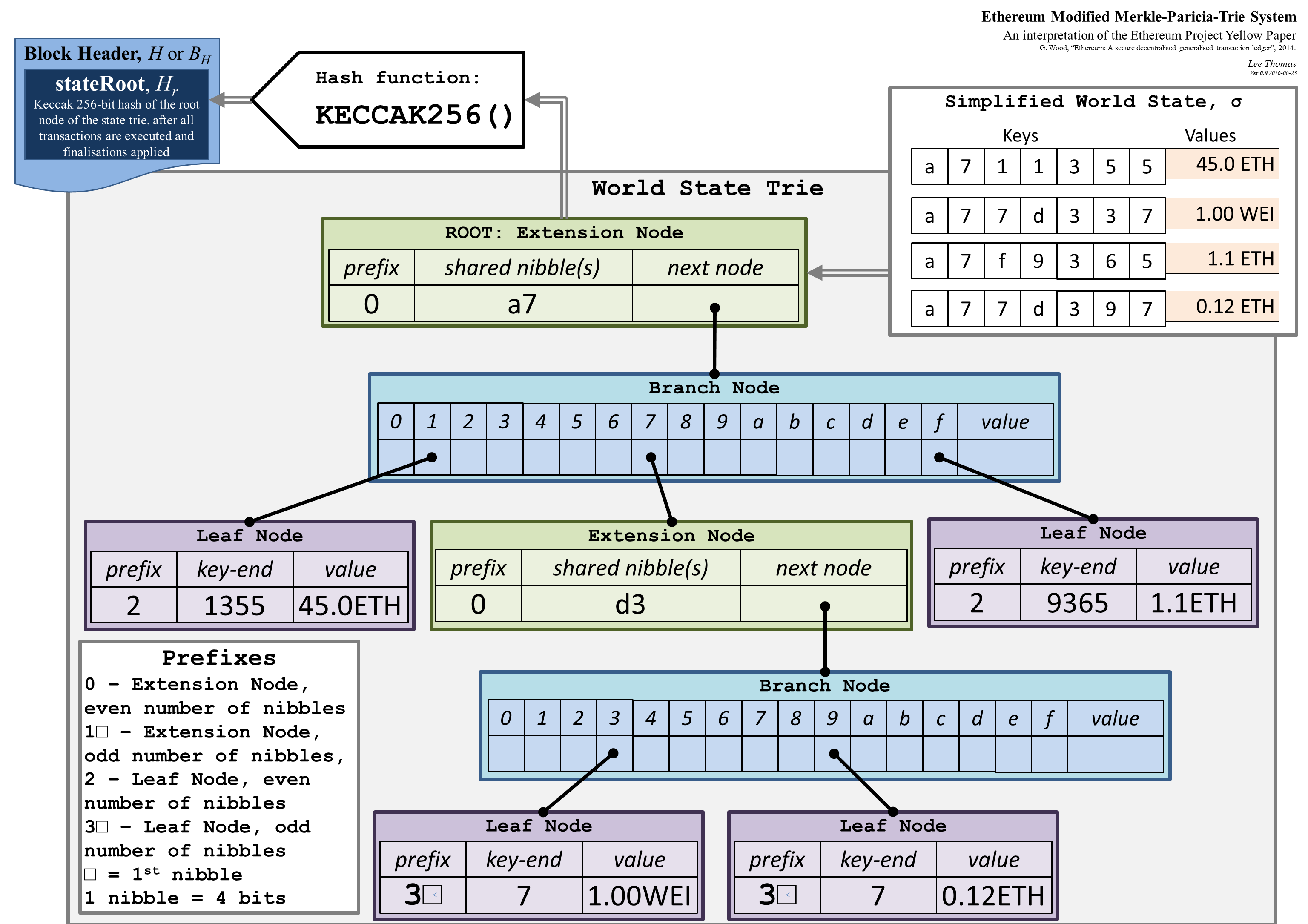
Use the upper 4 bits of the first byte of the []byte value composed of nibbles as storage flag. The 0th bit stores the parity information, and the 1st bit stores the type represented by the value
| hex char | bits | pointing to | odd/even | 2nd niddle padding |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0000 | node | even | no |
| 1 | 0001 | node | odd | yes |
| 2 | 0010 | value | even | no |
| 3 | 0011 | value | odd | yes |
this encoding method is only used when accessing the database. After reading into memory, the key is directly stored in []byte type
In the trie module, there is a Database object, which you can understand as a cache layer of the underlying database. In actual use, the Trie object uses the Database as a database. However, the important function of Database is not caching, but the reference counting of node data during caching, and provides Database.Reference and Database.Dereference to reference and dereference a trie node. If the reference count of a node becomes 0, the node will be deleted from memory, so it will not be written to the real database